Paris Olympics Kick Off: Can France Achieve a Double Win in the Medal Count and an Economic Boost?
As the countdown to the Paris 2024 Olympics reaches its final moments, all eyes turn to France. Will this iconic host nation not only shine on the podium but also reap the economic rewards?
The Paris 2024 Olympics is set to be one of the most significant global events of the decade. As the city gears up to host the Summer Games, the world watches with anticipation. In one hour, Paris will host the opening ceremony for the 2024 Olympics. Beyond the celebration, will France dominate the medal list this year? And will the French economy benefit from the Olympics?
This article delves into how the French athletes might fare on their home turf and explores whether hosting the Olympics will be a financial boon for Paris.
About the Paris 2024 Olympics: ‘the First’, ‘the Second’ and ‘the Greenest’
The First Gender Parity
Paris 2024 will be the first Olympics in history to achieve numerical gender parity on the field of play, with an equal number of female and male athletes participating in the largest sporting event in the world. Out of the 10,500 athletes participating in the Games, 5,250 will be men and 5,250 women.
‘The Second’ to Host the Olympics Three Times
The French capital will become the second city to host the Olympics three times (1900, 1924), after London (1908, 1948, and 2012). The 2024 Games will mark the return of the Olympics to Paris after 100 years
The ‘Greenest ever’
There will be no air conditioning in the athletes’ rooms at Paris 2024, which has pledged to host the “greenest ever” Games. Instead, buildings in the athletes’ village have been designed with a cooling system drawing water from underground, and facades adjusted so they get little direct sun.
Economic Impact of Hosting the Paris Olympics
Cost of Hosting the Olympics
Hosting the Olympics is a significant financial undertaking. The expenditures for the Paris 2024 Olympics include infrastructure development, security, operational costs, and more. Infrastructure projects such as the construction of new sports venues, the Olympic Village, and transportation upgrades are major cost drivers. Additionally, ensuring the safety of athletes, visitors, and residents demands substantial investment in security measures.
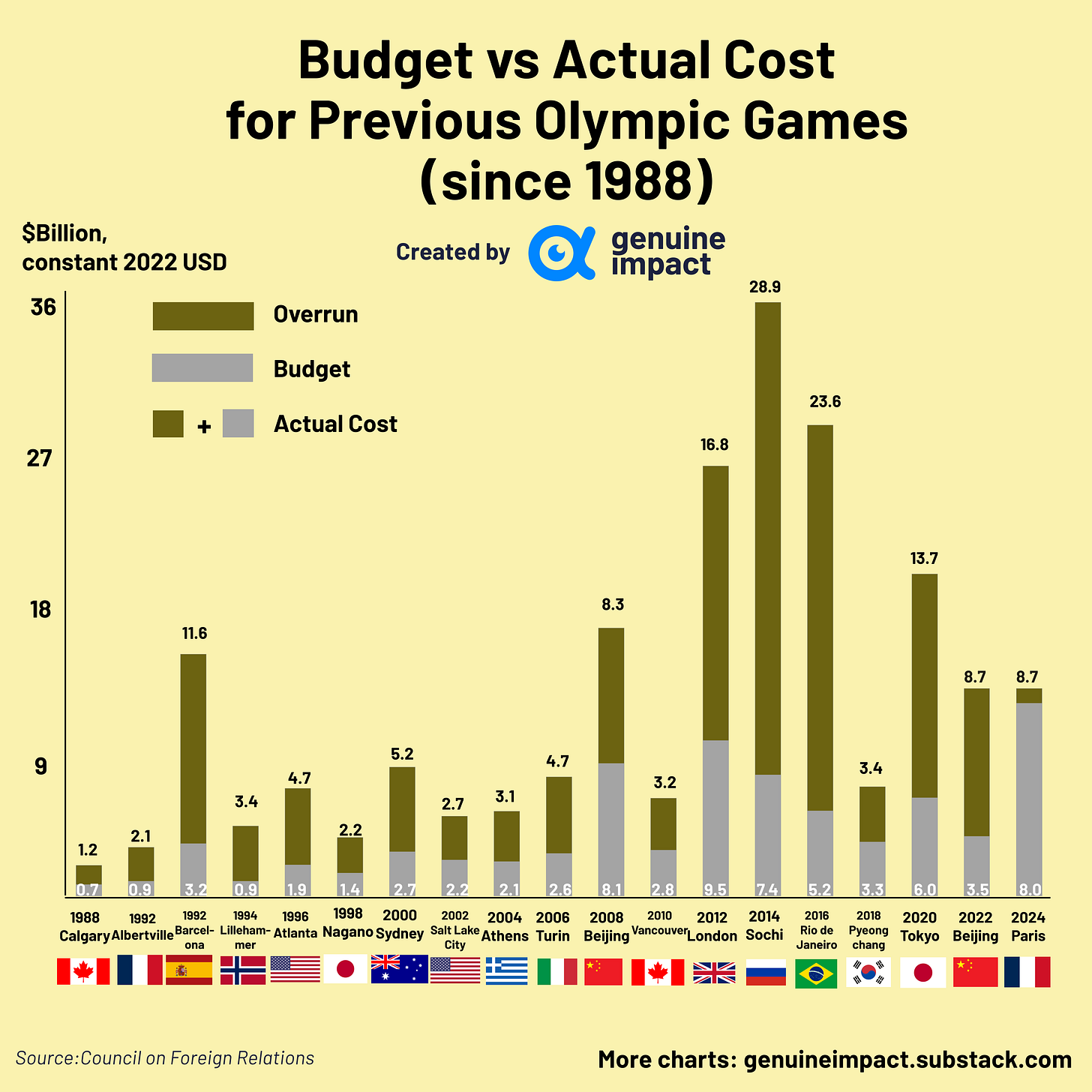
When Paris won its bid for the 2024 Olympics in 2017, it budgeted approximately $8 billion for the event. Since then, the budget has increased by 0.7 billion dollars. According to an S&P Global Ratings analysis, costs are divided fairly evenly between operating expenses and new infrastructure. If the final expenses remain within this range, Paris will host the cheapest Summer Games in decades.
Organizers attribute cost control to the strategic use of existing venues, such as those built for the annual French Open and the 2016 European Football Championship. Additionally, the games will be distributed across various stadiums in other French cities, including Lyon, Marseille, and Nice. Despite these measures, Paris has invested $4.5 billion in infrastructure, with $1.6 billion allocated for the Olympic Village, which is at least 33% over the initial budget.
Historically, cost overruns and budget deficits are common issues that can strain public finances. Recent Olympic Games have underscored the ongoing debate about the costs and benefits of hosting such mega-events. The 2020 Tokyo Olympics extended a decades-long trend of cost overruns, exacerbated by an unprecedented pandemic delay. Some former host cities are still grappling with debts, and thus they either withdraw their bids or scale back their plans in future games.
Revenue Streams
To offset these expenditures, Paris will rely on various revenue streams. Key sources of income include ticket sales, sponsorships, broadcasting rights, and merchandising. The sale of broadcasting rights is expected to be particularly lucrative, given the global interest in the Olympics. Sponsorship deals with multinational corporations will also play a critical role in funding the event.
Historically, the actual revenue from past Olympics has varied. For example, the London 2012 Olympics generated approximately $5.2 billion in revenue. Paris will need to exceed these figures to ensure a profitable outcome.
Short-term Economic Benefits
The Olympic Games are expected to bolster the French economy this year, according to the INSEE statistics institute. However, it cautions that France's volatile political situation could threaten these projections. INSEE forecasts that quarterly growth in the third quarter will accelerate to 0.5%, up from 0.3% in the previous quarter. The Olympics, scheduled for July and August, will contribute 0.3 percentage points to this growth through ticket sales, TV rights, and increased tourism.
Ideally, the short-term economic benefits of hosting the Olympics should be significant. Local businesses in the tourism, hospitality, and retail sectors are poised to benefit from the influx of visitors. Hotels, restaurants, and shops will likely see a surge in customers, boosting the local economy. Additionally, the preparation and execution of the event will create numerous job opportunities. From construction workers to service staff, the demand for labor will provide employment for thousands, contributing to lower unemployment rates in the short term.
Despite high hopes, the overall impact is more modest than anticipated due to rising travel and accommodation costs, political instability in France, and security concerns discouraging many sports fans, as reported by Reuters.
Flight bookings are expected to increase by 10% during the summer, according to flight ticketing data firm ForwardKeys. Nevertheless, like other popular tourist cities, Paris is already crowded and expensive. Most Olympic tourists merely replace traditional tourists who delay or cancel their trips. Additionally, some central city restaurants and shops are experiencing a drop in revenue ahead of the event due to security restrictions, as reported by France 2 and FRANCE 24.
Later this year, as the effect of the Paris Olympics diminishes, the French economy is expected to contract by 0.1% in the fourth quarter compared to the third quarter, according to INSEE. Consequently, annual GDP growth is projected to remain at 1.1% for this year, the same rate as in 2023, according to a Tuesday INSEE report titled "On GDP, Games, and Uncertainties".
Long-term Economic Gains
Beyond the immediate economic boost, the Olympics can create a lasting legacy. Infrastructure improvements, such as enhanced transportation systems and sports facilities, will benefit Paris long after the Games conclude. These upgrades can attract future international events and increase the city's global visibility.
Additionally, the international exposure from hosting the Olympics can boost long-term tourism. Visitors who come for the Games may return for leisure, and the city's enhanced reputation can attract new tourists globally.
"The effect would be similar to the one the London 2012 Olympics had on the British economy," said INSEE economist Dorian Roucher. The UK economy has seen a trade and industry boost in excess of £14 billion following the London 2012 Olympic and Paralympic Games, beating the 4-year target of £11 billion in half the time.
Debate: How Good is the Economic Effect?
Economists have found mixed impacts on tourism from the Olympics. Security concerns, crowding, and higher prices often deter visitors. Barcelona, which hosted in 1992, is often cited as a tourism success story, moving from the eleventh to the sixth most popular European destination post-Games. Sydney and Vancouver experienced slight tourism increases after hosting. However, some research showed that Beijing, London, and Salt Lake City saw tourism declines during their hosting years.
In Brazil, the first South American country to host the Olympics, the 2016 Rio Games' costs surpassed $20 billion, with the city of Rio alone shouldering at least $13 billion. Amidst a severe recession, Rio required a $900 million bailout from the federal government to cover policing costs and couldn't pay all its public employees. Significant investments in infrastructure aimed at revitalizing struggling neighborhoods have, post-Games, left most venues abandoned or underused.
Will France Dominate the Medal List?
What Determines the Success on the Medal List?
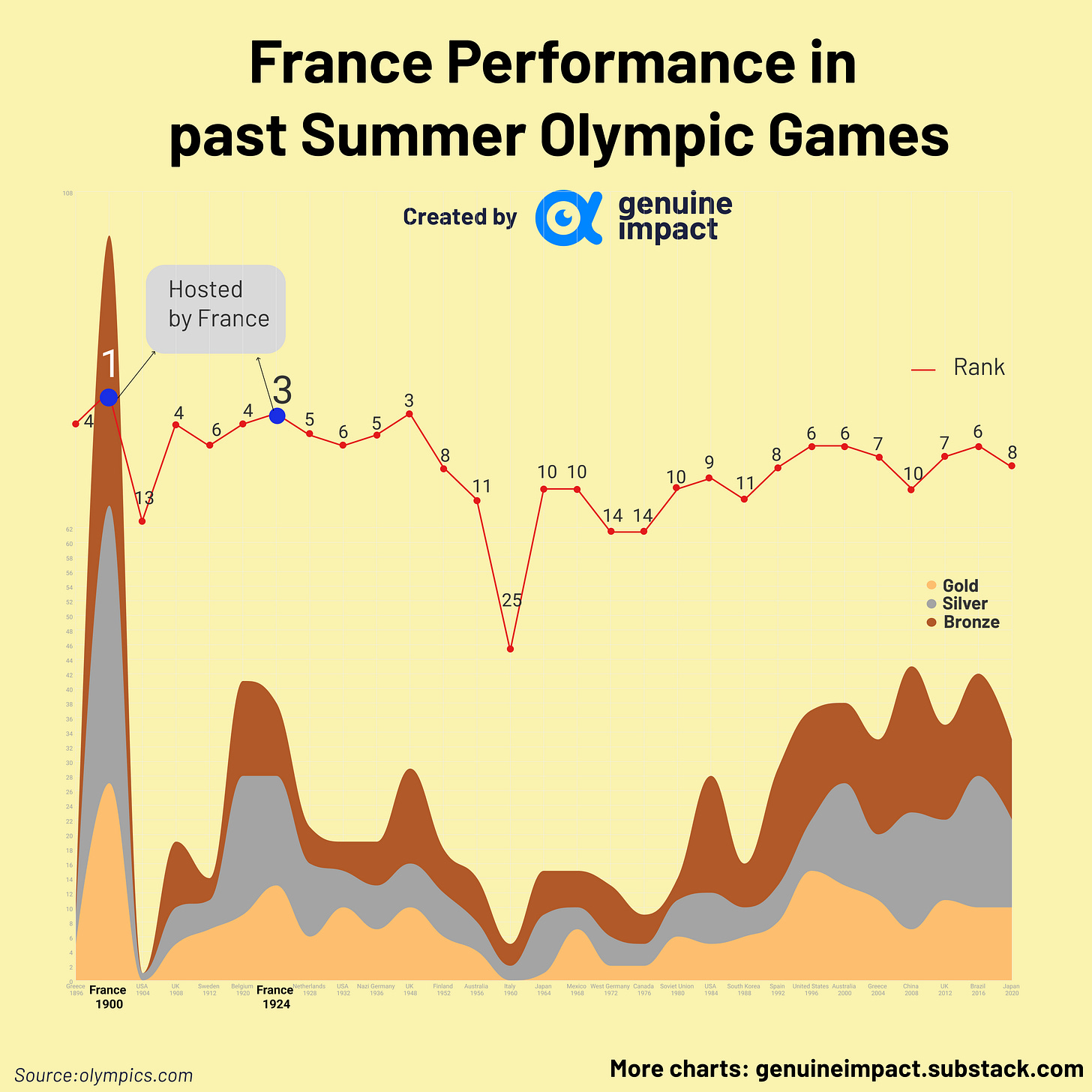
Total GDP is the best predictor of national Olympic performance, while population size, political ideology, and hosting the games are the determinants as well, summarised by researchers (Bernard and Busse, 2004). Rewilak (2021) indicated that the host effect influences Olympic success and is one of the most robust determinants. Historically, France performed quite well as a host in 1900 and 1924, placing 1st and 3rd respectively.
New Events Introduced by France
Host nations often introduce new events at the Olympics to showcase their strengths and increase their chances of winning medals. For example, Japan added softball and karate, where their athletes excelled and won gold medals.
This year, France has introduced breaking (breakdancing) and kayak cross as new events. While adding new sports does not guarantee more success for the host nation, it certainly increases their opportunities to win medals in these disciplines.
Prediction & For Investors
While France is expected to improve its medal count at the Summer Olympics this year, especially after their slight decline in Tokyo 2020, it is unlikely they will top the medal rankings at the 2024 games, given that China and the US often compete for the top spot.
Investors should closely monitor France's economic performance impacted by the Olympics, especially since this could be the most cost-effective summer game in decades. The financial burden on the host city might not be heavy, and the Olympics could stimulate the French economy amid the current political climate in France. In the future, it is important to observe the fluctuations in the stock market brought about by the progress of the French Olympics.
Created by Yiding & Shawn & Wendy