Where are we in the cycle? 📈📉
And why history often repeats itself
Business cycles are a fundamental aspect of any modern economy. These cycles are characterized by fluctuations in economic activity, including changes in GDP, employment, and inflation. Quite often history repeats itself through cycles. ‘This time is different’ turns out usually to be the same.
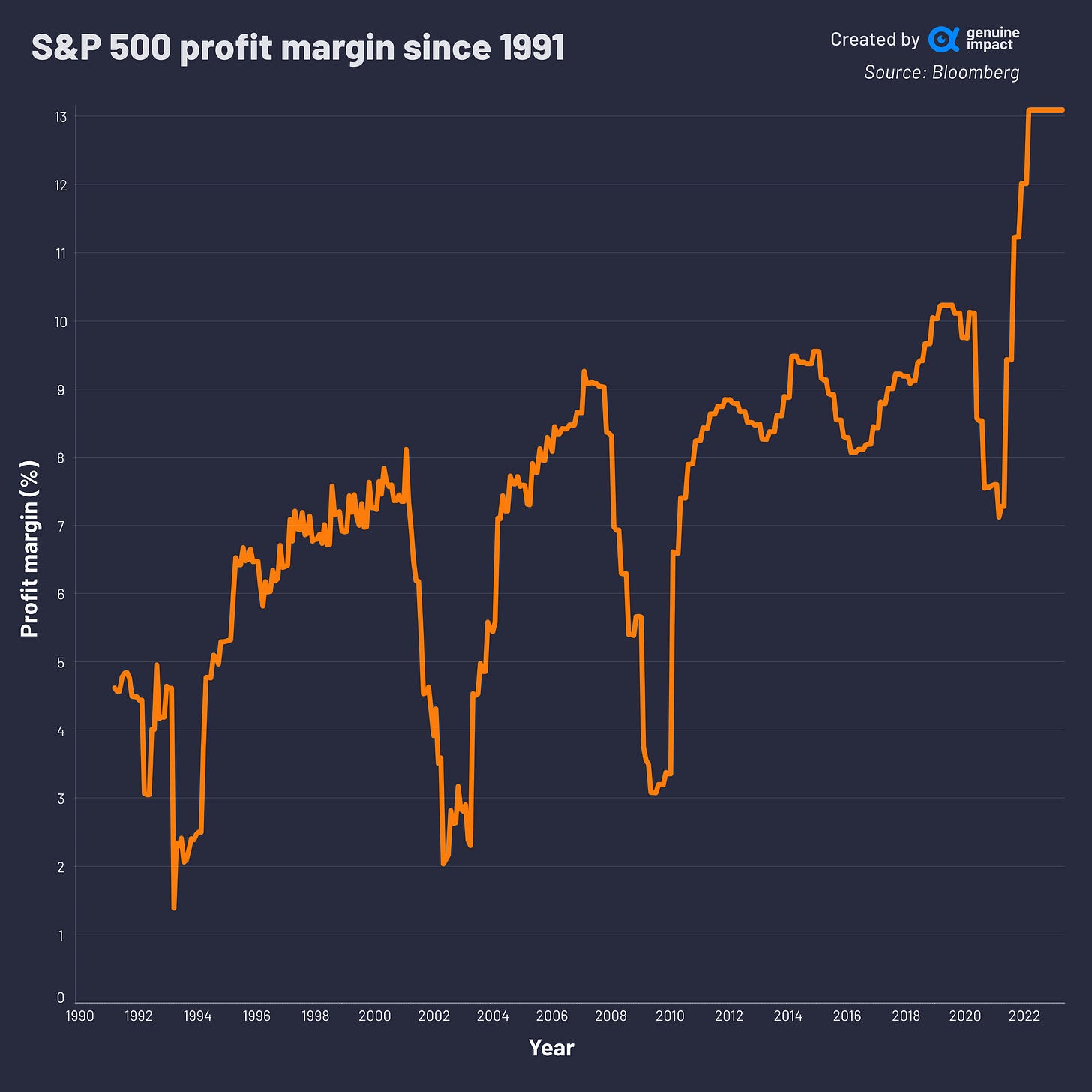
One way to measure the health of a business during these cycles is by looking at its net profit margin. When margins are high, businesses are able to reinvest in growth and innovation. However, during times of economic contraction, margins can become squeezed, leading to cost-cutting measures and potentially even bankruptcy.
Margins also tend to revert to a mean level, as shown here by the weighted average margin of companies in the S&P 500 index. This means that when margins are abnormally high, they are likely to fall back to more normal levels over time, and vice versa. Another interesting observation is the mean level after reversion may reset at a slightly different, in this case, higher level, over a long period of time.
Sponsored content
The future isn’t a mystery
Want to stay up to date on industry trends that drive the future?
You’re not alone — which is why we read TheFutureParty. Trusted by 200k+ driven professionals, their daily newsletter delivers stories that intersect between media, tech, and business. Don’t miss out on concise hot takes that are actually digestible and fun to read.
Let’s carry on.
There are generally two types of businesses: those that are non-cyclical, and those that are cyclical in nature. Non-cyclical businesses are those that provide products or services that are in demand regardless of the state of the economy. Examples of non-cyclical businesses include healthcare, utilities, and consumer staples such as pharmaceuticals, electricity, food, and household goods.
Cyclical businesses, on the other hand, are those that are heavily influenced by changes in the economy. These businesses tend to perform well during periods of economic growth and expansion but may struggle during economic downturns. Examples of cyclical businesses include sectors of consumer discretionary, energy, materials, and financials such as cars, petroleum, steel, and banks.
It’s clear that the margins for a cyclical business are much more volatile than a non-cyclical business, from this chart below. Non-cyclical sectors are consumer staples, healthcare, and utilities. Cyclical sectors are industrials, consumer discretionaries, financials, materials, energy, information technology, and communication services.
We have 10 more charts covering specific margin analysis for each business sector, with some of the largest and most important companies globally. They are our premium content, pay to unlock, and gain an edge on this topic of business cycles.
👀 To give you a sense of what the full article looks like, we snapshot of it below.
We have an earlybird special offer. But you only have until April 30th to grab it before it’s gone. You can reimburse it with your company here.